NORTHERN NEVADA’S
LEADING EYE DOCTORS IN RENO
Innovators in experienced, state-of-the-art medical and surgical care for the eyes.
MEDICAL AND SURGICAL SERVICES
Comprehensive Eye Exams in Reno
Just like an annual physical exam, an annual eye exam is very important to detect medical vision problems early and help prevent vision loss as you age. Comprehensive eye exams assess your entire visual system and overall eye health, and may include a combination of several different eye tests depending on age, health history, and risk factors for conditions like glaucoma and cataracts. It is important to note that a medical eye exam at Eye Care Professional is intended for early diagnosis and treatment of eye and vision problems to help prevent vision loss – we do not prescribe glasses or contacts. Vision problems that can effect long-term eye health often have no obvious signs or symptoms in their earliest stages. Comprehensive medical eye exams can help your eye doctor be more proactive than reactive when it comes to your vision health.
MEDICAL EYE EXAMS
OPHTHALMOLOGIST VS. OPTOMETRIST
You may be wondering why our office does not prescribe glasses or contacts as part of your eye exam. This is because at Eye Care Professionals, we have ophthalmologists who specialize in medical eye care to diagnose and treat eye conditions such as cataracts and glaucoma. Here is a breakdown:
- Ophthalmologists are medical doctors (MDs or DOs) trained to diagnose and treat eye diseases, including performing surgery.
- Optometrists (ODs) focus more on vision care, such as eye exams, glasses, contact lens prescriptions, and some disease management.
We partner with several optometry practices in Reno where we refer patients for refractions and prescriptions. While our office focus on the medical side, optometrists manage routine vision, which includes contacts and glasses prescriptions. If you need one of these referrals, our staff will be happy to help you with that at your next medical eye exam.

Comprehensive Medical Eye Exam Potential Tests
Patient History
Your eye doctor will ask about any vision problems you are currently experiencing or have experienced in the past. They will also ask about family history, medications, and other health conditions that may affect your eyes, like diabetes. They will also discuss with you any environmental or work-related conditions that can be detrimental to the eyes, such as prolonged computer work or smoking.
Visual Acuity
A visual acuity is an eye test that measures how clearly each eye is seeing. It usually involves an eye chart that starts with a large “E” and then works its way down to smaller letters, numbers and symbols. You will read these letters and symbols at a distance and near so the doctor can get a sense of your visual acuity. This is then measured in a fraction, for example 20/20, which is considered normal distance acuity. It means that you can see the smallest letter, 20 feet away. Additional tests are performed to determine what your best corrected acuity is as well.
Preliminary Tests
Your eye doctor will want to look at specific areas of visual function and eye health. These can include color vision, peripheral vision, the way your pupils respond to light, depth perception, and eye muscle movements.
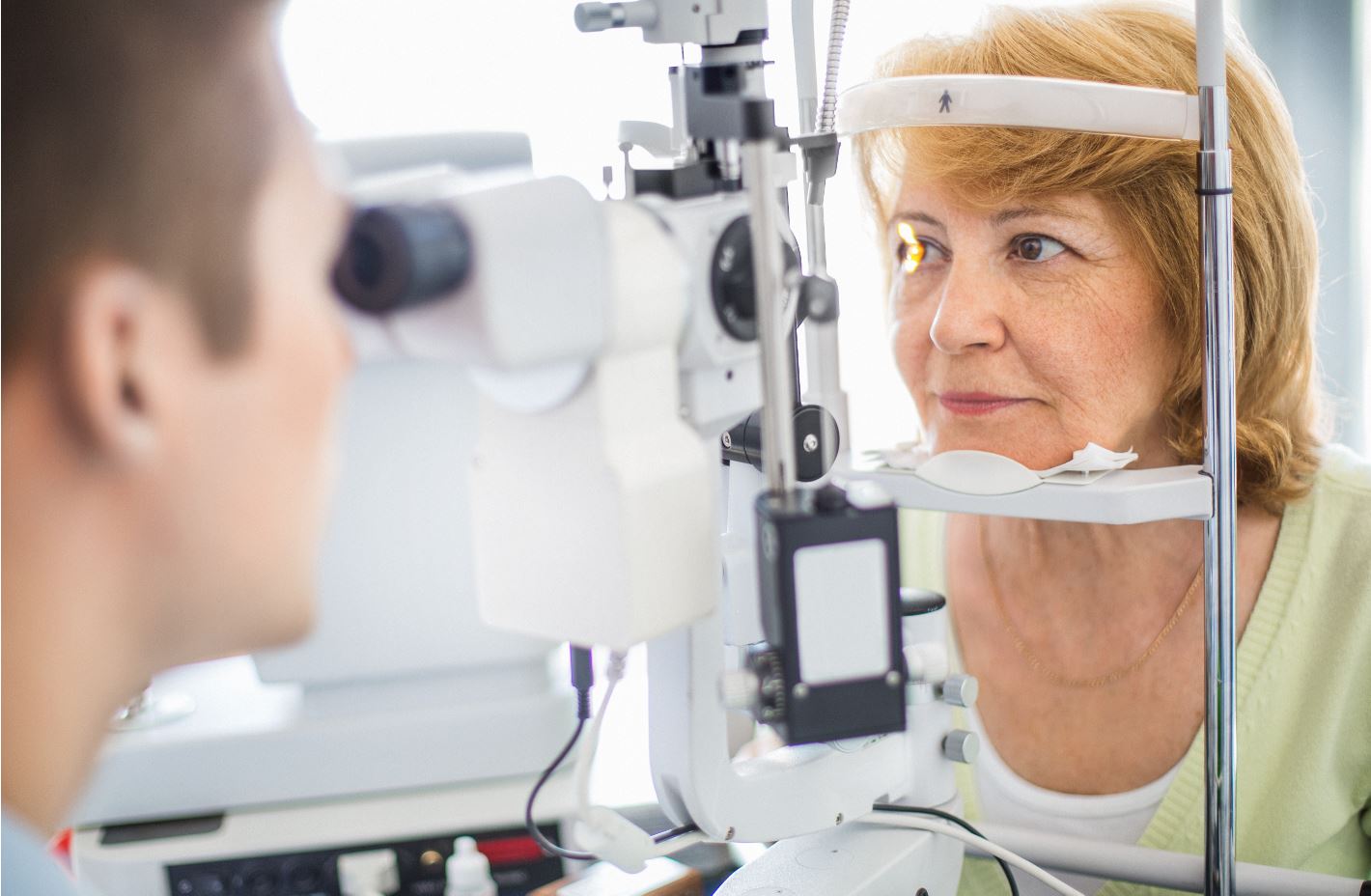
Additionally, your doctor will test for overall eye health. This is usually done with a Slit Lamp Test and sometimes requires dilation that widens the pupil to assess the health of all the structures of the eye and the surrounding tissues. The slit lamp allows the doctor to examine the internal and external parts of the eye in detail, such as the conjunctiva, iris, lens, cornea, retina and the optic nerve. The doctor looks into the eye with the slit lamp microscope, which is magnified with a high-intensity light. A slit lamp test enables the doctor to evaluate the eyes for signs of normal aging and eye pathology, such as conjunctivitis, cataracts, macular degeneration or retinal detachment. Early diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases are essential for preventing vision loss.
Keratometry/topography
These tests measure the curvature of the cornea (the clear outer surface of the eye) by focusing a circle of light on the cornea and measuring its reflection. This measurement is particularly critical in determining the proper fit for contact lenses.
Refraction
Refraction tests for any refractive error to determine the lens power needed to correct vision for any patient who does not have 20/20 vision. The most common refractive eye issues are nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. Your doctor will use a phoropter to place a series of lenses in front of your eyes, asking you which combination makes you see more clearly. Your input helps your eye doctor determine which lenses give you the clearest vision and therefore create a prescription for glasses or contacts.
Eye focusing, eye teaming, and eye movement testing
Your eyes have to move and work together to clearly see a single image. An assessment of accommodation, ocular motility, and binocular vision determines how well your eyes focus, move and work together. This eye movement testing will look for problems that keep eyes from focusing effectively or make it difficult to use both eyes together.
Tonometry
Tonometry is a test to detect glaucoma by measuring the pressure inside your eye or IOP (intraocular pressure). Glaucoma can cause vision loss and even blindness if the IOP in the eye is too high and damages the optic nerve.
The applanation tonometer, typically attached to a slit lamp, is one of the most common instruments used to measure the pressure in the eye. Prior to doing this test the doctor will numb the patient’s eyes using an anesthetic, before gently putting pressure on the patient’s cornea to measure the pressure in the eye.
Dilated Retinal Exams
An important part of any comprehensive eye exam is a retinal exam through a dilated pupil. This allows an assessment of the blood vessels, peripheral retina, macula and optic nerve. In addition, in many cases we will perform photography and other measurements of the retina, optic nerve, macula. Other instruments can be used to measure other elements of the visual system such as the cornea, the lens, the refractive error and overall dimensions of the eye.