Macular degeneration is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding this condition—its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options—is essential for preserving vision.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through what macular degeneration is, the symptoms to watch for, and the best ways to manage and prevent it.
What is Macular Degeneration?
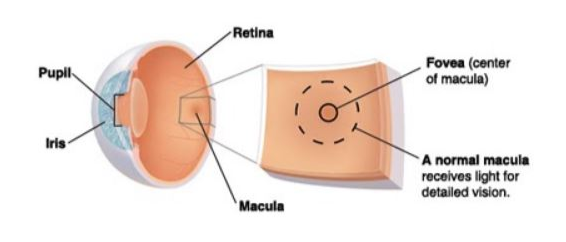
Macular degeneration, often referred to as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is a progressive eye disease that affects the macula, the central part of the retina. The macula is responsible for sharp, central vision, which is crucial for tasks such as reading, driving, and recognizing faces.
When the macula deteriorates, it leads to a gradual loss of central vision, though peripheral vision usually remains unaffected.
It is important to know that there are two main types of macular degeneration.
Dry Macular Degeneration
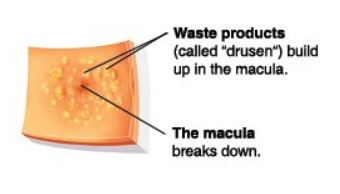
This is the most common form, accounting for around 80-90% of cases. It occurs when the light-sensitive cells in the macula slowly break down, causing gradual vision loss. Over time, dry macular degeneration may progress to advanced stages.
Wet Macular Degeneration
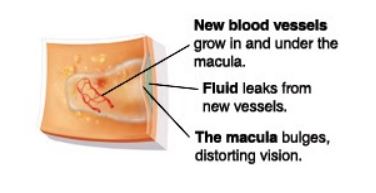 This less common but more severe form occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow under the retina and leak fluid or blood, leading to rapid vision loss. Wet AMD is more likely to cause severe central vision impairment.
This less common but more severe form occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow under the retina and leak fluid or blood, leading to rapid vision loss. Wet AMD is more likely to cause severe central vision impairment.
Symptoms of Macular Degeneration
The symptoms of macular degeneration can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease. However, the most common symptoms include:
- Blurry central vision
- Straight lines appear wavy
- Difficulty reading or seeing fine details
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of macular degeneration is not fully understood, several known risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing the condition. These include:
- Age: The most significant risk factor for macular degeneration is age. The condition primarily affects people over the age of 60, with the risk increasing as you get older. It is estimated that 1 in 3 people over the age of 75 have some form of AMD.
- Genetics: A family history of macular degeneration can increase your risk. Researchers have identified specific genes linked to AMD, suggesting that genetics plays a role in the development of the disease.
- Smoking: Smoking is a major modifiable risk factor for macular degeneration. It has been shown to increase the risk of developing AMD and can also accelerate the progression of the disease in individuals who already have it.
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can contribute to the development of macular degeneration by damaging the blood vessels in the eye. Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels can reduce the risk of vision loss.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels can also increase the risk of AMD by contributing to the buildup of plaque in blood vessels, including those in the eye.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of macular degeneration, particularly wet AMD, due to its effects on blood circulation and overall health.
Treatment Options
Currently, there is no cure for macular degeneration, but several treatment options can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Dry Macular Degeneration
There is no direct cure for dry macular degeneration, but certain treatments may help slow its progression. Doctors often recommend a combination of vitamins and antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, zinc, and beta-carotene, to support eye health. Studies have shown that these supplements can reduce the risk of advanced AMD in some individuals.
Wet Macular Degeneration
Treatment for wet macular degeneration is more advanced and may include:
Laser Therapy
This treatment uses focused laser light to destroy abnormal blood vessels under the retina, preventing further damage.
Anti-VEGF Injections
These injections block a protein called VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), which promotes the growth of abnormal blood vessels. Anti-VEGF medications, such as Avastin, Lucentis, and Eylea, are commonly used to slow the progression of wet AMD and improve vision in some patients.
While these treatments can help manage symptoms, they are not a cure and must be monitored regularly.
Prevention Tips
Although there is no surefire way to prevent macular degeneration, there are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce your risk:
- Regular eye exams
- Healthy lifestyle
- Sun protection
- Quit smoking
Choose Eye Care Professionals
Macular degeneration is a serious eye condition that can affect your vision and quality of life, but with early detection and proper care, its progression can be managed. By staying informed about the symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to protect your sight.
At Eye Care Professionals, we are committed to helping you preserve your vision for years to come. Our experienced team of ophthalmologists and optometrists offer personalized care and the most up-to-date treatments for macular degeneration. Whether you’re seeking a routine eye exam or specialized care, we are here to guide you every step of the way.
Why Choose Us?
- Protect and preserve
- Thorough and effective care
- Compassionate service
- Patient-centric approach
Choose Eye Care Professionals as your trusted partner in safeguarding your eye health and vision. Let us help you maintain a clear, healthy vision for a brighter tomorrow.